It is always good to be informed about your car, its mechanisms, and parts so that you become aware of all the maintenance principles and safety measures that you may take to protect yourself and prolong the distance that your car would travel. Batteries are one of the most essential parts of your car; how would we start our engines without them? Although car batteries are different in size and shape, their main design is similar to a great deal.
The basic design of modern car batteries is based on the principles of transforming chemical energy into electrical power. Hence we can call the car battery as an electrochemical device. After the battery creates this electrical power the attached cables transfer these charges to its destinations.
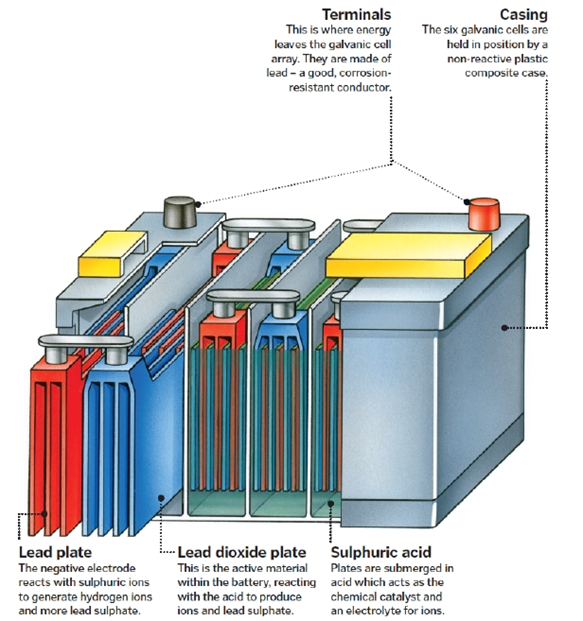
A basic 12-volt, lead-acid battery includes six cells connected in series. Each cell produces roughly two volts.
Electrolytes are the main component of the battery cells. It is worth mentioning here that an electrolyte is an ionized bath that generates an electrical current when required.
Furthermore, each cell contains plates that are made of active material and they are both positive and negative. The positive plates contain lead dioxide (PbO2), while the negative plates contain straight lead (Pb). Molded polypropylene is the main material that constitutes the battery case.
A plate group holds a number of plates of the same charge (positive or negative). They are made to a post strap. The plate groups then alternate within the battery; positive, negative… Usually, a car battery would contain an extra set of negative plates to balance the charge. Separators are sheets made of non-conductive material that and are inserted between the plates to ensure that the different groups do not touch each other.
A battery mainly performs two main cycles, the charge and discharge cycles. In the discharge cycle, a chemical process takes place inside the battery in which the lead (Pb) of the negative plates combines with the SO4 of the sulfuric acid to produce lead sulfate (PbSO4). In this process, the electrolyte becomes weaker and the positive and negative plates become more neutral. At this stage, the battery loses power
Because the charge of a battery depends on the difference between the two plate component materials and the concentration of the electrolyte, and because this difference decreases during discharging,
On the other hand, the charge cycle is the reverse process. Electrical current, generated by the car’s alternator, passes through the plates, forcing SO4 back into the electrolyte bath and elevating specific gravity, which increases voltage.
For more information about sell used cars, please visit